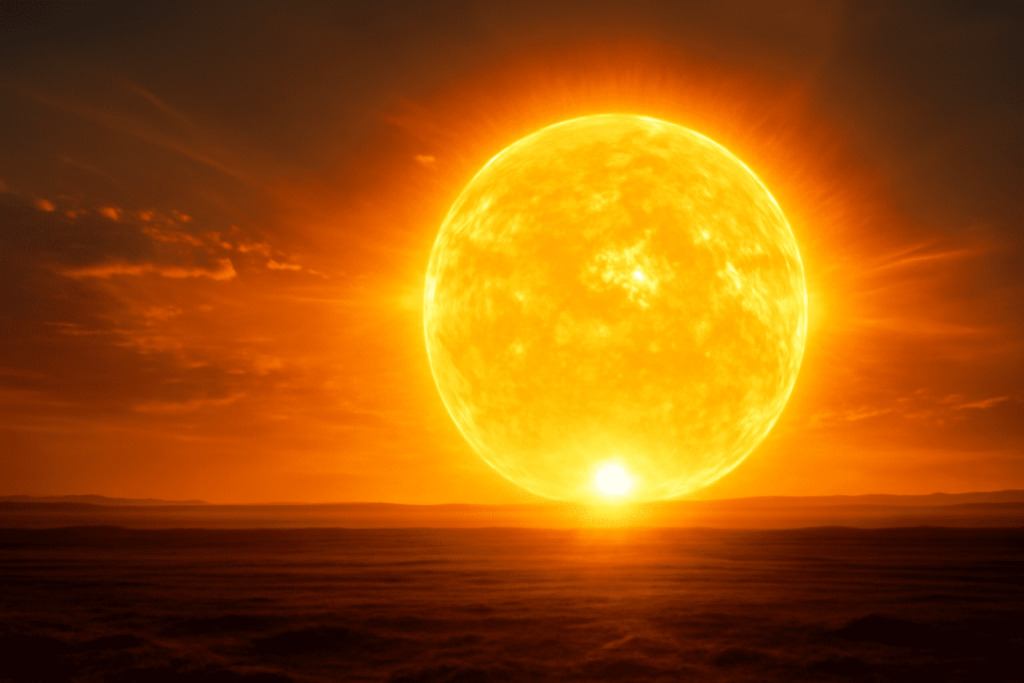
The Sun is far more than just a bright ball of light in the sky. It is an incredibly complex star that plays a crucial role in the existence of life on Earth. Despite its importance, the Sun is still full of mysteries and surprising facts that many of us don’t fully understand. These 10 fascinating facts about the Sun will completely change the way you view our closest star and the essential role it plays in the cosmos.
1. The Sun Makes Up 99.86% of the Mass in Our Solar System
The Sun is the undisputed heavyweight champion of the solar system, accounting for a staggering 99.86% of the total mass. That means everything else—planets, moons, comets, and asteroids—make up only 0.14% of the solar system’s mass. It’s no wonder the Sun has such a powerful influence on everything that orbits it.
2. The Sun is a Giant Nuclear Reactor
At the Sun’s core, nuclear fusion occurs. Hydrogen atoms are fused together under extreme pressure to form helium, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process. This is the power source behind the Sun’s light and heat, and every second, the Sun converts about 4.2 million tons of matter into energy. The Sun’s nuclear reactions are responsible for all the energy we receive on Earth, from the warmth we feel to the light that powers our days.
3. The Sun is Actually White, Not Yellow
While the Sun may appear yellow, especially from Earth’s surface, it is actually white when viewed from space. This is because the Sun emits all the colors of the visible spectrum equally, creating white light. The yellow or red hues we see on Earth are due to the scattering of shorter wavelengths (like blue and violet) by our atmosphere, leaving the longer wavelengths (red, yellow, and orange) to dominate the sky.
4. The Sun’s Energy Takes Thousands of Years to Reach Earth
Although sunlight reaches us in about 8 minutes, the energy created at the Sun’s core takes a long time to make its way to the surface. The process of radiative diffusion means it takes around 100,000 years for energy to travel from the core to the outer layers of the Sun. Once the energy reaches the photosphere, it can travel freely through space and reach Earth in just a few minutes.
5. The Sun’s Corona is Hotter Than Its Surface
It seems strange, but the Sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the corona, is much hotter than the surface of the Sun itself. The photosphere, the visible surface of the Sun, has a temperature of around 5,500°C (9,932°F), but the corona reaches temperatures of 1-3 million°C (1.8-5.4 million°F). Scientists are still puzzled as to why the corona is so much hotter than the Sun’s surface, making this one of the Sun’s most enduring mysteries.
6. The Sun is Shrinking, but It Won’t Affect Us for Billions of Years
Over time, the Sun has been losing mass, converting hydrogen into helium in its core. It loses about 4.1 million tons of mass every second, but don’t worry—this won’t lead to any drastic changes for a long time. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will start to expand, eventually turning into a red giant. By then, it will be much larger than it is today, possibly engulfing the inner planets, including Earth.
7. The Sun’s Magnetic Field is Unpredictable
The Sun has an incredibly powerful magnetic field that affects not just the Sun itself, but also the entire solar system. The Sun’s magnetic field flips every 11 years during its solar cycle, and this shift causes fluctuations in solar activity, including solar flares and sunspots. These solar events can affect space weather and cause disruptions in satellite communication and power grids here on Earth.
8. Solar Flares Can Disrupt Technology
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation from the Sun’s surface. When directed at Earth, these flares can affect Earth’s magnetosphere, creating geomagnetic storms that disrupt satellites, GPS systems, and even electrical grids. A large enough solar flare could potentially cause widespread communication and technology failures, making them a real concern for space weather scientists.
9. The Sun Has a Family of Planets and Other Objects
The Sun is not alone in space; it has a family of objects that orbit it, including eight major planets, several dwarf planets, and countless asteroids and comets. The Sun’s gravity holds these objects in place, creating the structure of our solar system. Without the Sun, none of these objects would be able to maintain their orbits or even exist in the first place.
10. The Sun Will Eventually Die, but Not for Billions of Years
The Sun, like all stars, will eventually run out of fuel. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will exhaust its hydrogen supply and expand into a red giant. During this phase, it will burn off its outer layers and shed them into space, leaving behind a dense core that will cool over time, becoming a white dwarf. This will mark the end of the Sun’s life, but don’t worry—the process will take billions of years, and we’ll have plenty of time to enjoy its warmth and light before then.
Conclusion: A Powerful and Mysterious Star
The Sun is not just the source of life and light for Earth; it’s an incredibly complex and powerful star with many mysteries still waiting to be uncovered. From its immense size to its unpredictable magnetic field, the Sun has a profound impact on our solar system and everything within it. Understanding these strange facts about the Sun helps us appreciate the forces that make our world—and our universe—function.